Hello friends,
This is very easy and general article applied by any Normal Internet user.

Lets begin with a short intro of a web browser:
A web browser is an application software program used for displaying, interacting with images, text and other information located on a website.
Each web page has a unique address called a URL, or Universal Resource Locator, which tells where a particular file or information is located among all the computers that are part of the Internet.
What Happen while browsing?
Most of the Internet user suffer from their Browser when they open lots of tab(10-15),by doing so their browser speed becomes slow and they blaim their Internet Service Providers for slow speed and some times their browser also crashes.
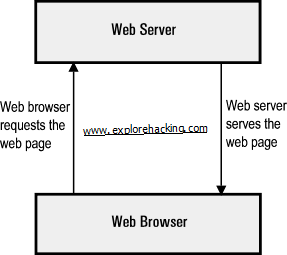
How Browser Works?
When we open any website from our web Browser(IE,Mozilla etc.) then our Browser works as client and it requests to a webserver and in turn webserver responses(or to locate) the query of client and return the information to the client (web browser)i.e. open the site.
There are many hidden properties in web browser which ordinary user can't get easily or by googling.
So,now I am exposing some of the properties of Mozilla which helps the you to increase its speed and prevent from crashing.
You can boost up your Mozilla speed now
1) Type about:config in the address bar and click go or press Enter.
You may get a warning like that:

Hit Enter:-)
2) You get a huge table consist of many fields(preference name,value etc.) like that:
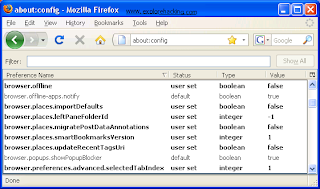
3) In the filter search bar type "network.http.pipelining".Its value field (Default) has "false" value.Now, double-click to it and set its value to "true".
Reason for it:
HTTP is the application-layer protocol that most web pages are transferred with it. In HTTP 1.1, multiple requests can be sent before any responses are received. This is known as pipelining. Pipelining reduces page loading times, but not all servers support it.
4) Go back to the filter search bar and type "network.http.pipelining.maxrequests".Double-click to it and set its value to "8".
5) In the filter search bar and again type "network.http.proxy.pipelining". Its value field (Default)has "false" value.Now, double-click to it and set its value to "true".
6)Go back to the filter search bar and type "network.dns.disableIPv6".Set this option to true by double clicking on it.
Reason for it:
In IPv6-capable DNS servers, an IPv4 address may be returned when an IPv6 address is requested. It is possible for Mozilla to recover from this misinformation, but a significant delay is introduced.
Feel free to ask any queries in comments.
This is very easy and general article applied by any Normal Internet user.

Lets begin with a short intro of a web browser:
A web browser is an application software program used for displaying, interacting with images, text and other information located on a website.
Each web page has a unique address called a URL, or Universal Resource Locator, which tells where a particular file or information is located among all the computers that are part of the Internet.
What Happen while browsing?
Most of the Internet user suffer from their Browser when they open lots of tab(10-15),by doing so their browser speed becomes slow and they blaim their Internet Service Providers for slow speed and some times their browser also crashes.
How Browser Works?
When we open any website from our web Browser(IE,Mozilla etc.) then our Browser works as client and it requests to a webserver and in turn webserver responses(or to locate) the query of client and return the information to the client (web browser)i.e. open the site.

There are many hidden properties in web browser which ordinary user can't get easily or by googling.
So,now I am exposing some of the properties of Mozilla which helps the you to increase its speed and prevent from crashing.
You can boost up your Mozilla speed now
1) Type about:config in the address bar and click go or press Enter.
You may get a warning like that:

Hit Enter:-)
2) You get a huge table consist of many fields(preference name,value etc.) like that:

3) In the filter search bar type "network.http.pipelining".Its value field (Default) has "false" value.Now, double-click to it and set its value to "true".
Reason for it:
HTTP is the application-layer protocol that most web pages are transferred with it. In HTTP 1.1, multiple requests can be sent before any responses are received. This is known as pipelining. Pipelining reduces page loading times, but not all servers support it.
4) Go back to the filter search bar and type "network.http.pipelining.maxrequests".Double-click to it and set its value to "8".
5) In the filter search bar and again type "network.http.proxy.pipelining". Its value field (Default)has "false" value.Now, double-click to it and set its value to "true".
6)Go back to the filter search bar and type "network.dns.disableIPv6".Set this option to true by double clicking on it.
Reason for it:
In IPv6-capable DNS servers, an IPv4 address may be returned when an IPv6 address is requested. It is possible for Mozilla to recover from this misinformation, but a significant delay is introduced.
Thank you for reading :)
Feel free to ask any queries in comments.








No comments:
Post a Comment