skip to main |
skip to sidebar

iPhone users whose devices have been stolen may soon get a little help from Apple when it comes to the problem of iMessages going to the pilfered phone. Ars has heard that Apple may be planning changes to the way iMessages are handled that will make it simpler for users to lock out unauthorized devices, though it's unclear when that might happen. In the meantime, some users are finding that there are some temporary "fixes" to the problem of iMessages going to stolen phones.
Ars covered this phenomenon last week when Ars reader David Hovis contacted us to tell us his wife's tale of woe. To recap: Mrs. Hovis' iPhone 4S was stolen, so she remotely wiped the device and then asked her carrier to deactivate the SIM. She then purchased a new iPhone and activated it with her old number—theoretically erasing all traces of her information from the original stolen phone. But when Hovis began sending iMessages to his wife, both she and the new owner of the stolen phone received them—Hovis and the new owner had a somewhat lengthy dialogue back and forth about the issue in order to confirm, and the new owner (who had allegedly purchased the stolen device from someone for $500) seemed just as perplexed as Hovis.
Several threads posted online recounted similar horror stories, and after publishing our piece, we received e-mails from a number of other affected users. One user who contacted us was deeply concerned that someone she knew as a stalker might have stolen her iPhone, and that all iMessages directed at her (on a new phone) were also going to the stalker. Clearly, this can turn into a major concern for some iPhone users.
I recommend reading Jesse Hollington's Google+ post (and the corresponding comments) on how to set a PIN on your SIM; it contains the default SIM codes for most of the popular carriers in the US and Canada. Please note that the SIM PIN trick won't work for Verizon iPhones—there is no SIM, and you can potentially lock yourself out much easier if you try to set a PIN for your nonexistent card. (Read the comment by Josh Schoenwald in the aforementioned Google+ post to find out what happens when you try to do this. Don't feel bad, Josh—you're helping everyone else learn!)
Still, our sources tell us that performing the aforementioned three-step process (remote wipe, deactivation, then activation on a new SIM) should work from this point on to lock out a stolen iPhone. So if you find yourself having some bad luck with thieves, it's worth trying that method before trying to set a PIN on your SIM card.
We'll keep you updated if and when we hear anything new about this issue, and please keep e-mailing me with your stories and observations about iMessage.

“I don’t want to say we’re making our own Facebook. But, we’re making our own Facebook,” said Ed Knutson, a web and mobile app developer who joined a team of activist-geeks redesigning social networking for the era of global protest.
They hope the technology they are developing can go well beyond Occupy Wall Street to help establish more distributed social networks, better online business collaboration and perhaps even add to the long-dreamed-of semantic web — an internet made not of messy text, but one unified by underlying meta-data that computers can easily parse.
The impetus is understandable. Social media helped pull together protesters around the globe in 2010 and 2011. Egyptian dictator Hosni Mubarak so feared Twitter and Facebook that he shut down Egypt’s internet service. A YouTube video posted in the name of Anonymous propelled Occupy Wall Street from an insider meme to national news. And top-trending Twitter hashtags turned Occupy from a ho-hum rally on Sept. 17 into a national and even international movement.
Now it’s time for activists to move beyond other people’s social networks and build their own, according to Knutson.
“We don’t want to trust Facebook with private messages among activists,” he said.
The same thinking applies to Twitter and other social networks — and the reasoning became clear last week, when a Massachusetts district attorney subpoenaed Twitter for information about the account @OccupyBoston and other accounts connected to the Boston movement. (To its credit, Twitter has a policy of giving users the opportunity to contest such orders when possible.)
“Those networks will be perfectly fine — until they are not. And it will be a one-day-to-the-next thing,” said Sam Boyer, an activist turned web developer, turned activist again, who works with the New York City occupation’s tech team.
A move away from mainstream social networks is already happening on several levels within the Occupy movements — from the local networks already set up for each occupation to an in-progress, overarching, international network project called Global Square, that Knutson is helping to build. Those networks are likely to be key to Occupy’s future, since nearly all of the largest encampments in the United States have been evicted — taking with them the physical spaces where activists communicated via the radically democratic General Assemblies.
The idea of an open alternative to corporate-owned social networking sites isn’t novel — efforts to build less centralized, open source alternatives to Facebook and Twitter have been in the works for years, with the best known examples being Diaspora and Identica.
But those developments aren’t specifically focused on protest movements. And the Occupy movement’s surprising rise in the U.S. has added new impetus to the desire for open source versions of the software that is playing an increasingly important role in mobilizing and connecting social movements, as well as broadcasting their efforts to the world.
One challenge that all of the new efforts face is a very difficult one for non-centralized services: ensuring that members are trustworthy. That’s critical for activists who risk injury and arrest in all countries and even death in some. To build trust, local and international networks will use a friend-of-a-friend model in Knutson and Boyer’s projects. People can’t become full members on their own as they can with social networks like Twitter, Facebook and Google+.
“You have to know someone in real life who sponsors you,” said Knutson.
To Boyer, it’s more important to identify someone as trustworthy than to ensure that their online name matches a passport or birth certificate.
“I respect pseudonyms as long as they treat them as pseudonyms and not as masks,” said Boyer. In other words, someone shouldn’t hide behind a fake name to get away with bad behavior — in an extreme case, infiltrating the movement to spy on or sabotage it.
Thirty-six-year-old Knutson, who lives in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, started the year as an observer of politics before evolving into a committed OWS activist. His metamorphosis started during public-employee strikes in February against proposed policies of Governor Scott Walker that would affect their benefits and collective-bargaining rights.
“Before this year we had the idea that things maybe were starting to improve a little,” he said. “But when things started happening in February we were like, ‘No, no. Things are getting worse.’”
While organizing a “Walkerville” protest camp in June, Knutson met, over Twitter, members of Spanish protest movement 15M. They had just built a web site, Take the Square, to track occupations around the world, from Tunisia to Madrid. He also met Alexa O’Brien – founder of campaign-finance-reform organization US Day of Rage and a co-founder of Occupy Wall Street. After OWS kicked off, Knutson came to the East Coast for a while, visiting New York, Boston and Philadelphia and joining with other techies in those cities.
Through all those connections, Knutson has focused on building the technology for an international occupations network. But the politics are tricky. “Some of the people in Spain are kind of resentful of OWS, because they got all of the credit,” he said, noting that the Spanish occupations started first and are still far bigger.
As a counterpart to Knutson, Sam Boyer focuses on the US occupations, building tech for a collection of interlinked social networks across the country with the working title Federated General Assembly, or FGA. Working on Occupy has brought him full-circle.
When he was an undergrad in 2005, Boyer, who is now 27, took a job at the Student Trade Justice Campaign, an organization focused on trade policy reform. In 2007, he wanted to build an online platform for individual chapters to organize into groups and to link those groups for national discussions – essentially what the FGA is meant to do. But Boyer couldn’t build it, he said. “I didn’t even know how to program at the point that I started with it.”
So Boyer started learning, and falling in love with, Web programming; and he switched from being mainly an activist to mainly an engineer. His specialty is an open-source content-management system for web sites called Drupal, which FGA will run on.
Knutson, Boyer and the other Occupy geeks don’t have to build everything from scratch. “These are standards that have been around for a while, and we are not reinventing the wheel,” said Boyer.
For instance, the projects will rely on set of technologies known as Open ID and OAuth that let a user sign into a new website using their logins and passwords from social networks like Facebook, Google and Twitter. Those technologies let you sign up for a new service by logging into a Twitter or Google account, which vouch for you to the new site without giving over your password or forcing you to get yet another username and password to keep track of.
In the new OWS tech, an activist’s local-occupation network can vouch for a user to another network, and the local networks all trust each other, they all trust that activist. Someone can sign into one network and post and comment on them all.
Some sensitive posts, say about civil disobedience, would be private. Others, like a statement of demands or press release, would be public, but only trusted members of the network could create them.
FGA wants to differentiate itself from the the me-me-me narcissism of Facebook. It has a strong focus on groups — working together on topics like alternative banking or electoral reform.
And there’s a lot of work today. Currently, the group aspects of Occupy web sites are a cacophony.
“You get there, and the first thing you look at is this useless activity feed,” said Boyer. Every comment – whether a brilliant idea, a troll comment or a me-too pile-on – pops into the list as it’s generated. “You’re only guaranteed that one person really thought that post was a good idea – not the whole group,” he said.
In the FGA system, each group has a discussion on what information to push to their home page, such as a description of an event, a blog post or minutes from a meeting. “In the same way that, when you look at Reddit, you know that the articles on top are the most upvoted, the user could know that posts appearing on a front page represent the concerted agreement of the group,” said Boyer.
The activist coders also want to be able to push and pull info to and from the rest of the movement. The idea is that they can have disparate systems that label info with shared tags that will, some day, make it possible to enter a search on any one site and pull precise results from around the world.
Ed Knutson’s job is to get those sites talking to each other, even though the content may be in different languages (English, Spanish, Arabic, etc.) and created with different content management systems, or CMSs, such as Drupal or Wordpress. The Global Square network will connect not through those systems but through “semantic Web” standards designed to link up disparate technologies.
One key standard has the wordy name Resource Description Framework, or RDF, a universal labeling system.
If an occupier wants to post the minutes of a meeting, for example, they might type them in the appropriate text box in the content management software running the site. That software pushes the information to an RDF database and tags it with some universal label – it could be called “minutes” or any other term that all the occupations agree on. The local occupier might also select “Group: Alternative Banking” from a dropdown list, and that label would be added as well. Using the same labels allows all the sites to trade information. So a search for minutes from an Alternative Banking group would pull up records from any occupation with that kind of group.
With RDF, sites can work together even if they run on different content management software, such as Drupal (as in the FGA) or Wordpress (as in the Spanish M15 group).
“The handoff point is that everything goes through RDF,” said Knutson. “You don’t care if they have a Drupal site or some kind of Frankenstein combination of different stuff.”
The problem the coders face will be the same one that’s faced the web for years – getting people to agree on standards and to then adopt them. One long-running attempt to do this quickly is called Microformats – a way of including markup data in HTML that’s invisible to an human visitor, but which can be understood by their browser or by a search engine. Examples include marking up contact information so that a reader can simply click contact information to add it to their address book and annotating a recipe so that search engines can let you search for recipes that include ’spinach’.
These linkage and collaboration capabilities would be useful well beyond the Occupy movement.
“I think any type of small or medium-sized group or a team that has one person in eight different cities,” could use it for collaboration, says Knutson. And he sees no reason against spinning off the tech to businesses.
“Every small and medium business owner is a member of the 99%,” said Knutson. “Furthermore, exploring relationships with businesses… is pretty important to having a tangible impact.”
“A lot of what we are tying to do is build a better conversation so that this cacophonous discussion can be more coordinated,” said Boyer. As an analogy, he recounted an OWS workshop from a conference on December 18 in New York City when the moderator asked everyone to shout out their best idea for the movement.
They were probably all good ideas, said Boyer. But he couldn’t hear any one of them through the noise of the others.
The Web of trust among networks, RDF labels that link data across occupations, working-group consensus on what to post – all are designed to help the right people connect to each other and to the right information. “Let the sheer number of people who are interested get out the way of the many things actually happening,” said Boyer.
But for now, all those ideas are just that – ideas. And whatever does emerge will come piecemeal.
Sam Boyer hopes to launch in the following weeks what he calls a stepping stone — a roster of occupations around the world called, for now, simply directory.occupy.net. M15’s Take the Square site has provided something like that since May, as have other sites. But directory.occupy.net will be unique in using RDF and other technologies to label all the entries. It will also allow people from each occupation to “own” and update their entries.
“The directory should be useful, but it’s not our big debut,” said Boyer. He’s hoping that will be sometime in the spring, when a rough version of the FGA social network launches.
The Global Square Knutson is helping to build is finalizing its tech and will launch, probably in January, with basic linkages for various Occupy sites to trade messages, re-publish articles and allow cross-commenting on them.
“I’d say it would be a pretty major accomplishment to get a couple of the [web site] systems that everyone is using, like ELGG and Drupal and media wiki and maybe Wordpress” to work together, he said.
But even just having the discussion has been a big deal. “It’s hard to get people to even think about that kind of stuff.”
Source-
Wired

Postal workers, department store clerks and elves aren’t the only ones working like crazy this holiday season. For Bryan Sartin, it’s the busiest time of year.
Sartin is a director of investigative response with Verizon Business. He’s the guy you call when you’ve been hacked and he usually doesn’t get much of a Christmas vacation.
“Right before big holidays, particularly Christmas and New Year’s is when the very vast majority of people seem to find out that they’ve been hacked,” he says. “We’ll do as much as 20 percent of our annual caseload during this part of December.”
In 2010, about 92 percent of those cases involved criminals trying to steal money over the internet, but this year everything changed.
The first signs emerged in December 2010, when activists with the online collective Anonymous called for digital sit-ins — known as distributed denial of service attacks — on the websites of companies that had refused to process payments for Wikileaks. Then, in early 2011, attacks on Sony, HBGary and many law enforcement agencies hit the headlines. None of them appear to have been financially motivated.
That’s meant big changes in the kinds of threats that companies are preparing for.
Sartin helps compile a widely watched yearly study of data breaches, and he says that hacktivist and state-sponsored attacks will show up in this year’s report, big time. “That trend has certainly continued this year and it will embody itself in a big way in our upcoming study.”
But for all the high-profile LulzSec and Anonymous attacks this year, Sartin still believes the hacktivist threat — long ignored by corporate IT — is now frequently overhyped.
He says clients often approach Verizon after they see a Twitter message or an internet post threatening an attack on a pre-determined day. The company gears up for an event, bringing consultants on site, and ordering technical staff to be at the ready.
It’s not cheap, and most of the time, nothing happens. “Very commonly, when companies are receiving these kinds of threats in advance, no one ever makes good on them,” he says.
Last year, reported cyber-threats to the New York Stock Exchange, the Federal Reserve, and Facebook never materialized.
In one actual attack — Sartin wouldn’t name the company — criminals broke in and got access to a database filled with encrypted client data. Looking at the logs, Verizon investigators could see that the attackers had downloaded all of the encrypted data — something that would force the company to notify its customers that their data had been accessed. But they didn’t download the one most useful table of all — an unencrypted list of the encryption keys that could be used to decrypt all of the data they had stolen.
“They were stealing data with no interest in deciphering the encryption,” he says. “They were just stealing it to force this company into making a disclosure.”
While the hacktivists may be overhyped, Sartin says they’re often better than the other hackers out there. According to him, many attacks that are thought to be state sponsored, are surprisingly unsophisticated. Known as advanced persistent threat attacks, Sartin calls them “awfully persistent, but not so advanced.”
There’s one more surprise that will show up in the 2012 Data Breach Report, which will include a lot more data sources from Europe and Asia than previous reports.
“In this part of the world, China is the source of a lot of our crimes, but if you go to China … the U.S. is the number one source of electronic crimes,” Sartin says. “Over here we think that all of these advanced persistent threats and things come from China. Over there, they think they all come from here.”

Microsoft comes up with innovation in log-in method now you can use any of the pictures as your login. There is not pre set pictures you can grab any of your favorite pictures and set it at your login. Many of us don’t remember our text passwords ether they are difficult or mix up with your other passwords so to have a picture as your log-in is an easy solution which is more user friendly. It seems that this is majorly designed for touch screen devices but desktop users can also avail this facility. How you can set this picture log-in is select any picture then select the part you want as your password. When you will turn on your computer it will ask for password if there is any picture set you have to tap that specific area to get login or draw line or connect the parts to get login or enclose any specific part. These are only three methods restricted to enter your password. It does not mean if you set any picture as your login then you cannot use text password at the same time. You can keep both options if you failed to enter the correct part of the picture as your password, after five attempts you will get block until you enter text password.

This is not only user friendly but more attractive than conventional way of entering passwords. Microsoft says, “When you draw either a circle or a line on your selected picture, Windows remembers how you drew it,” Pace said. “So, someone trying to reproduce your picture password needs to not only know the parts of the image you highlighted and the order you did it in, but also the direction and start and end points of the circles and lines that you drew.”
It is as protected as your text passwords; it cannot compromise on your security. So you can use this feature with full confidence. This is best safeguarding mechanism so one can rely on this. Picture password is fast, fluid, secure and robust promising security system. But you cannot use this feature on remote system or in any complete network. It is currently available in “Developer view”. You can try this amazing and cool feature on your systems.
Please share your comments and reviews about this exceptional feature in Windows8; I will be waiting for your comments. Stay tuned and Happy Reading


To be eligible, it will exceed the 20,000 customers who are connected to the first phase and 750 000 for the second phase. This fiber will be drawn to a length of 300 km between Stockholm and Jönköping, thus taking all subscribers of this operator between the two cities. Telia is responsible for the fiber and equipment such as Cisco CRS-3, high-speed router that can handle up to 322 Tb / s.





 A panic button or boss key application performs one or multiple actions when the button is activated. This usually includes hiding a window, but sometimes other things such as muting the volume.
A panic button or boss key application performs one or multiple actions when the button is activated. This usually includes hiding a window, but sometimes other things such as muting the volume.


- Find out what I'm doing, Follow Me :)
Saturday, December 31, 2011
iMessages going to stolen iPhones? There may be a fix in the works

iPhone users whose devices have been stolen may soon get a little help from Apple when it comes to the problem of iMessages going to the pilfered phone. Ars has heard that Apple may be planning changes to the way iMessages are handled that will make it simpler for users to lock out unauthorized devices, though it's unclear when that might happen. In the meantime, some users are finding that there are some temporary "fixes" to the problem of iMessages going to stolen phones.
Ars covered this phenomenon last week when Ars reader David Hovis contacted us to tell us his wife's tale of woe. To recap: Mrs. Hovis' iPhone 4S was stolen, so she remotely wiped the device and then asked her carrier to deactivate the SIM. She then purchased a new iPhone and activated it with her old number—theoretically erasing all traces of her information from the original stolen phone. But when Hovis began sending iMessages to his wife, both she and the new owner of the stolen phone received them—Hovis and the new owner had a somewhat lengthy dialogue back and forth about the issue in order to confirm, and the new owner (who had allegedly purchased the stolen device from someone for $500) seemed just as perplexed as Hovis.
Several threads posted online recounted similar horror stories, and after publishing our piece, we received e-mails from a number of other affected users. One user who contacted us was deeply concerned that someone she knew as a stalker might have stolen her iPhone, and that all iMessages directed at her (on a new phone) were also going to the stalker. Clearly, this can turn into a major concern for some iPhone users.
The "fixes"
So what is a worried iPhone user to do to protect yourself? There's a growing consensus that there are indeed some ways to prevent iMessages from going to the wrong place, though some of the proposed solutions directly conflict with what some of the affected users have told Ars. Our friends at Macworld posted an article on Thursday claiming that a simple three-step process should help prevent this from happening:Macworld can confirm that perhaps the easiest way to ensure that a stolen phone stops receiving iMessages is to remotely wipe the phone, and then call your carrier and instruct them to deactivate your old SIM. The third and final step? Activate a new SIM in your new phone.We were unable to test this ourselves, so we're taking Macworld at their word—I spoke with the author of the piece, Lex Friedman, who told me he tested it personally with success. I went back to speak with Hovis with this article in hand, however, and he told me that he performed those same steps in the same order without success—the messages still went through to the owner of the stolen phone. Our only guess is that Apple has already made some changes to iMessage on the server side between the time Hovis performed his remote wipe and the time Friedman performed his remote wipe, but this remains unconfirmed.
Completing those three steps—wiping, deactivating your old SIM, and then activating a new one—ensures that your iMessages will get sent only to you and your iOS devices, and not anywhere else.
Setting a SIM PIN
There is another, slightly more complicated process that will also work to lock out stolen iPhones from your iMessages, but be warned: it could also block you from finding the phone via Find My iPhone if the thief reboots your phone. You can set a PIN on your SIM card, which is different than setting a PIN for the phone. The reason this is a less-ideal solution isn't just because it's more complicated—it's also because each carrier already has a default PIN set for your SIM card, and you risk locking yourself out from your own account if you don't do this correctly.I recommend reading Jesse Hollington's Google+ post (and the corresponding comments) on how to set a PIN on your SIM; it contains the default SIM codes for most of the popular carriers in the US and Canada. Please note that the SIM PIN trick won't work for Verizon iPhones—there is no SIM, and you can potentially lock yourself out much easier if you try to set a PIN for your nonexistent card. (Read the comment by Josh Schoenwald in the aforementioned Google+ post to find out what happens when you try to do this. Don't feel bad, Josh—you're helping everyone else learn!)
Still, our sources tell us that performing the aforementioned three-step process (remote wipe, deactivation, then activation on a new SIM) should work from this point on to lock out a stolen iPhone. So if you find yourself having some bad luck with thieves, it's worth trying that method before trying to set a PIN on your SIM card.
We'll keep you updated if and when we hear anything new about this issue, and please keep e-mailing me with your stories and observations about iMessage.
Source:
Friday, December 30, 2011
Occupy Geeks Are Building a Facebook for the 99%

Protesters volunteering for the internet and information boards of the Occupy Wall Street protest work and broadcast from their media center in Zuccotti Plaza on Oct. 2, 2011. Photo: Bryan Derballa for Wired.com
“I don’t want to say we’re making our own Facebook. But, we’re making our own Facebook,” said Ed Knutson, a web and mobile app developer who joined a team of activist-geeks redesigning social networking for the era of global protest.
They hope the technology they are developing can go well beyond Occupy Wall Street to help establish more distributed social networks, better online business collaboration and perhaps even add to the long-dreamed-of semantic web — an internet made not of messy text, but one unified by underlying meta-data that computers can easily parse.
The impetus is understandable. Social media helped pull together protesters around the globe in 2010 and 2011. Egyptian dictator Hosni Mubarak so feared Twitter and Facebook that he shut down Egypt’s internet service. A YouTube video posted in the name of Anonymous propelled Occupy Wall Street from an insider meme to national news. And top-trending Twitter hashtags turned Occupy from a ho-hum rally on Sept. 17 into a national and even international movement.
Now it’s time for activists to move beyond other people’s social networks and build their own, according to Knutson.
“We don’t want to trust Facebook with private messages among activists,” he said.
The same thinking applies to Twitter and other social networks — and the reasoning became clear last week, when a Massachusetts district attorney subpoenaed Twitter for information about the account @OccupyBoston and other accounts connected to the Boston movement. (To its credit, Twitter has a policy of giving users the opportunity to contest such orders when possible.)
“Those networks will be perfectly fine — until they are not. And it will be a one-day-to-the-next thing,” said Sam Boyer, an activist turned web developer, turned activist again, who works with the New York City occupation’s tech team.
A move away from mainstream social networks is already happening on several levels within the Occupy movements — from the local networks already set up for each occupation to an in-progress, overarching, international network project called Global Square, that Knutson is helping to build. Those networks are likely to be key to Occupy’s future, since nearly all of the largest encampments in the United States have been evicted — taking with them the physical spaces where activists communicated via the radically democratic General Assemblies.
The idea of an open alternative to corporate-owned social networking sites isn’t novel — efforts to build less centralized, open source alternatives to Facebook and Twitter have been in the works for years, with the best known examples being Diaspora and Identica.
But those developments aren’t specifically focused on protest movements. And the Occupy movement’s surprising rise in the U.S. has added new impetus to the desire for open source versions of the software that is playing an increasingly important role in mobilizing and connecting social movements, as well as broadcasting their efforts to the world.
One challenge that all of the new efforts face is a very difficult one for non-centralized services: ensuring that members are trustworthy. That’s critical for activists who risk injury and arrest in all countries and even death in some. To build trust, local and international networks will use a friend-of-a-friend model in Knutson and Boyer’s projects. People can’t become full members on their own as they can with social networks like Twitter, Facebook and Google+.
“You have to know someone in real life who sponsors you,” said Knutson.
To Boyer, it’s more important to identify someone as trustworthy than to ensure that their online name matches a passport or birth certificate.
“I respect pseudonyms as long as they treat them as pseudonyms and not as masks,” said Boyer. In other words, someone shouldn’t hide behind a fake name to get away with bad behavior — in an extreme case, infiltrating the movement to spy on or sabotage it.
Thirty-six-year-old Knutson, who lives in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, started the year as an observer of politics before evolving into a committed OWS activist. His metamorphosis started during public-employee strikes in February against proposed policies of Governor Scott Walker that would affect their benefits and collective-bargaining rights.
“Before this year we had the idea that things maybe were starting to improve a little,” he said. “But when things started happening in February we were like, ‘No, no. Things are getting worse.’”
While organizing a “Walkerville” protest camp in June, Knutson met, over Twitter, members of Spanish protest movement 15M. They had just built a web site, Take the Square, to track occupations around the world, from Tunisia to Madrid. He also met Alexa O’Brien – founder of campaign-finance-reform organization US Day of Rage and a co-founder of Occupy Wall Street. After OWS kicked off, Knutson came to the East Coast for a while, visiting New York, Boston and Philadelphia and joining with other techies in those cities.
Through all those connections, Knutson has focused on building the technology for an international occupations network. But the politics are tricky. “Some of the people in Spain are kind of resentful of OWS, because they got all of the credit,” he said, noting that the Spanish occupations started first and are still far bigger.
As a counterpart to Knutson, Sam Boyer focuses on the US occupations, building tech for a collection of interlinked social networks across the country with the working title Federated General Assembly, or FGA. Working on Occupy has brought him full-circle.
When he was an undergrad in 2005, Boyer, who is now 27, took a job at the Student Trade Justice Campaign, an organization focused on trade policy reform. In 2007, he wanted to build an online platform for individual chapters to organize into groups and to link those groups for national discussions – essentially what the FGA is meant to do. But Boyer couldn’t build it, he said. “I didn’t even know how to program at the point that I started with it.”
So Boyer started learning, and falling in love with, Web programming; and he switched from being mainly an activist to mainly an engineer. His specialty is an open-source content-management system for web sites called Drupal, which FGA will run on.
Knutson, Boyer and the other Occupy geeks don’t have to build everything from scratch. “These are standards that have been around for a while, and we are not reinventing the wheel,” said Boyer.
For instance, the projects will rely on set of technologies known as Open ID and OAuth that let a user sign into a new website using their logins and passwords from social networks like Facebook, Google and Twitter. Those technologies let you sign up for a new service by logging into a Twitter or Google account, which vouch for you to the new site without giving over your password or forcing you to get yet another username and password to keep track of.
In the new OWS tech, an activist’s local-occupation network can vouch for a user to another network, and the local networks all trust each other, they all trust that activist. Someone can sign into one network and post and comment on them all.
Some sensitive posts, say about civil disobedience, would be private. Others, like a statement of demands or press release, would be public, but only trusted members of the network could create them.
FGA wants to differentiate itself from the the me-me-me narcissism of Facebook. It has a strong focus on groups — working together on topics like alternative banking or electoral reform.
And there’s a lot of work today. Currently, the group aspects of Occupy web sites are a cacophony.
“You get there, and the first thing you look at is this useless activity feed,” said Boyer. Every comment – whether a brilliant idea, a troll comment or a me-too pile-on – pops into the list as it’s generated. “You’re only guaranteed that one person really thought that post was a good idea – not the whole group,” he said.
In the FGA system, each group has a discussion on what information to push to their home page, such as a description of an event, a blog post or minutes from a meeting. “In the same way that, when you look at Reddit, you know that the articles on top are the most upvoted, the user could know that posts appearing on a front page represent the concerted agreement of the group,” said Boyer.
The activist coders also want to be able to push and pull info to and from the rest of the movement. The idea is that they can have disparate systems that label info with shared tags that will, some day, make it possible to enter a search on any one site and pull precise results from around the world.
Ed Knutson’s job is to get those sites talking to each other, even though the content may be in different languages (English, Spanish, Arabic, etc.) and created with different content management systems, or CMSs, such as Drupal or Wordpress. The Global Square network will connect not through those systems but through “semantic Web” standards designed to link up disparate technologies.
One key standard has the wordy name Resource Description Framework, or RDF, a universal labeling system.
If an occupier wants to post the minutes of a meeting, for example, they might type them in the appropriate text box in the content management software running the site. That software pushes the information to an RDF database and tags it with some universal label – it could be called “minutes” or any other term that all the occupations agree on. The local occupier might also select “Group: Alternative Banking” from a dropdown list, and that label would be added as well. Using the same labels allows all the sites to trade information. So a search for minutes from an Alternative Banking group would pull up records from any occupation with that kind of group.
With RDF, sites can work together even if they run on different content management software, such as Drupal (as in the FGA) or Wordpress (as in the Spanish M15 group).
“The handoff point is that everything goes through RDF,” said Knutson. “You don’t care if they have a Drupal site or some kind of Frankenstein combination of different stuff.”
The problem the coders face will be the same one that’s faced the web for years – getting people to agree on standards and to then adopt them. One long-running attempt to do this quickly is called Microformats – a way of including markup data in HTML that’s invisible to an human visitor, but which can be understood by their browser or by a search engine. Examples include marking up contact information so that a reader can simply click contact information to add it to their address book and annotating a recipe so that search engines can let you search for recipes that include ’spinach’.
These linkage and collaboration capabilities would be useful well beyond the Occupy movement.
“I think any type of small or medium-sized group or a team that has one person in eight different cities,” could use it for collaboration, says Knutson. And he sees no reason against spinning off the tech to businesses.
“Every small and medium business owner is a member of the 99%,” said Knutson. “Furthermore, exploring relationships with businesses… is pretty important to having a tangible impact.”
“A lot of what we are tying to do is build a better conversation so that this cacophonous discussion can be more coordinated,” said Boyer. As an analogy, he recounted an OWS workshop from a conference on December 18 in New York City when the moderator asked everyone to shout out their best idea for the movement.
They were probably all good ideas, said Boyer. But he couldn’t hear any one of them through the noise of the others.
The Web of trust among networks, RDF labels that link data across occupations, working-group consensus on what to post – all are designed to help the right people connect to each other and to the right information. “Let the sheer number of people who are interested get out the way of the many things actually happening,” said Boyer.
But for now, all those ideas are just that – ideas. And whatever does emerge will come piecemeal.
Sam Boyer hopes to launch in the following weeks what he calls a stepping stone — a roster of occupations around the world called, for now, simply directory.occupy.net. M15’s Take the Square site has provided something like that since May, as have other sites. But directory.occupy.net will be unique in using RDF and other technologies to label all the entries. It will also allow people from each occupation to “own” and update their entries.
“The directory should be useful, but it’s not our big debut,” said Boyer. He’s hoping that will be sometime in the spring, when a rough version of the FGA social network launches.
The Global Square Knutson is helping to build is finalizing its tech and will launch, probably in January, with basic linkages for various Occupy sites to trade messages, re-publish articles and allow cross-commenting on them.
“I’d say it would be a pretty major accomplishment to get a couple of the [web site] systems that everyone is using, like ELGG and Drupal and media wiki and maybe Wordpress” to work together, he said.
But even just having the discussion has been a big deal. “It’s hard to get people to even think about that kind of stuff.”
Source-
Wired
2011 is the Year of the Hacktivist, Verizon Report Suggests

Verizon Business's Bryan Sartin, who investigates corporate break-ins, saw red this year over hacktivist threats to clients.
Postal workers, department store clerks and elves aren’t the only ones working like crazy this holiday season. For Bryan Sartin, it’s the busiest time of year.
Sartin is a director of investigative response with Verizon Business. He’s the guy you call when you’ve been hacked and he usually doesn’t get much of a Christmas vacation.
“Right before big holidays, particularly Christmas and New Year’s is when the very vast majority of people seem to find out that they’ve been hacked,” he says. “We’ll do as much as 20 percent of our annual caseload during this part of December.”
In 2010, about 92 percent of those cases involved criminals trying to steal money over the internet, but this year everything changed.
The first signs emerged in December 2010, when activists with the online collective Anonymous called for digital sit-ins — known as distributed denial of service attacks — on the websites of companies that had refused to process payments for Wikileaks. Then, in early 2011, attacks on Sony, HBGary and many law enforcement agencies hit the headlines. None of them appear to have been financially motivated.
That’s meant big changes in the kinds of threats that companies are preparing for.
Sartin helps compile a widely watched yearly study of data breaches, and he says that hacktivist and state-sponsored attacks will show up in this year’s report, big time. “That trend has certainly continued this year and it will embody itself in a big way in our upcoming study.”
But for all the high-profile LulzSec and Anonymous attacks this year, Sartin still believes the hacktivist threat — long ignored by corporate IT — is now frequently overhyped.
He says clients often approach Verizon after they see a Twitter message or an internet post threatening an attack on a pre-determined day. The company gears up for an event, bringing consultants on site, and ordering technical staff to be at the ready.
It’s not cheap, and most of the time, nothing happens. “Very commonly, when companies are receiving these kinds of threats in advance, no one ever makes good on them,” he says.
Last year, reported cyber-threats to the New York Stock Exchange, the Federal Reserve, and Facebook never materialized.
In one actual attack — Sartin wouldn’t name the company — criminals broke in and got access to a database filled with encrypted client data. Looking at the logs, Verizon investigators could see that the attackers had downloaded all of the encrypted data — something that would force the company to notify its customers that their data had been accessed. But they didn’t download the one most useful table of all — an unencrypted list of the encryption keys that could be used to decrypt all of the data they had stolen.
“They were stealing data with no interest in deciphering the encryption,” he says. “They were just stealing it to force this company into making a disclosure.”
While the hacktivists may be overhyped, Sartin says they’re often better than the other hackers out there. According to him, many attacks that are thought to be state sponsored, are surprisingly unsophisticated. Known as advanced persistent threat attacks, Sartin calls them “awfully persistent, but not so advanced.”
There’s one more surprise that will show up in the 2012 Data Breach Report, which will include a lot more data sources from Europe and Asia than previous reports.
“In this part of the world, China is the source of a lot of our crimes, but if you go to China … the U.S. is the number one source of electronic crimes,” Sartin says. “Over here we think that all of these advanced persistent threats and things come from China. Over there, they think they all come from here.”
Source:
Use your picture to log in into Windows8

Microsoft comes up with innovation in log-in method now you can use any of the pictures as your login. There is not pre set pictures you can grab any of your favorite pictures and set it at your login. Many of us don’t remember our text passwords ether they are difficult or mix up with your other passwords so to have a picture as your log-in is an easy solution which is more user friendly. It seems that this is majorly designed for touch screen devices but desktop users can also avail this facility. How you can set this picture log-in is select any picture then select the part you want as your password. When you will turn on your computer it will ask for password if there is any picture set you have to tap that specific area to get login or draw line or connect the parts to get login or enclose any specific part. These are only three methods restricted to enter your password. It does not mean if you set any picture as your login then you cannot use text password at the same time. You can keep both options if you failed to enter the correct part of the picture as your password, after five attempts you will get block until you enter text password.

This is not only user friendly but more attractive than conventional way of entering passwords. Microsoft says, “When you draw either a circle or a line on your selected picture, Windows remembers how you drew it,” Pace said. “So, someone trying to reproduce your picture password needs to not only know the parts of the image you highlighted and the order you did it in, but also the direction and start and end points of the circles and lines that you drew.”
It is as protected as your text passwords; it cannot compromise on your security. So you can use this feature with full confidence. This is best safeguarding mechanism so one can rely on this. Picture password is fast, fluid, secure and robust promising security system. But you cannot use this feature on remote system or in any complete network. It is currently available in “Developer view”. You can try this amazing and cool feature on your systems.
Please share your comments and reviews about this exceptional feature in Windows8; I will be waiting for your comments. Stay tuned and Happy Reading
Thursday, December 29, 2011
How to tag a friend or a page on Facebook on mobile devices or with Javascript turned off
Its been long since Facebook let users tag their friends or like pages in status updates or comments. The feature first came to status updates and later on to comments as well. You can simply type the @ symbol and start typing the name of your friend and select one from the autocomplete. But this feature won’t work if you are using Facebook from a mobile browser that doesn’t support Javascript or if Javascript is turned off on your browser. But still, you can tag your friends using an alternate method.
You can tag your friends on browsers that don’t support Javascript as well. But to do this, you need to remember the profile ID of your Facebook friend. On the status update text box type the following:
@ [138558659573745:0]
Replace the number before “:0” with the profile ID of your friend. You can find the profile id of any of your friend by copying it off their Facebook profile page. The Facebook profile page URL looks something like this:
http://www.facebook.com/profile.php?id=1742756183
But this trick doesn’t work for those who have already set their Facebook usernames. You can also use this trick for tagging Facebook fan pages.
You can tag your friends on browsers that don’t support Javascript as well. But to do this, you need to remember the profile ID of your Facebook friend. On the status update text box type the following:
@ [138558659573745:0]
Replace the number before “:0” with the profile ID of your friend. You can find the profile id of any of your friend by copying it off their Facebook profile page. The Facebook profile page URL looks something like this:
http://www.facebook.com/profile.php?id=1742756183
But this trick doesn’t work for those who have already set their Facebook usernames. You can also use this trick for tagging Facebook fan pages.
Virus protection tips: from basic to advanced level
Computer viruses or spam ware can steal your personal information, cause destruction with normal computer operations and attract new spam ware. Even, they can shut down your computer’s hard drive. Protecting your computer from viruses is critical for browsing success and safe computing. There are some virus protection tips for you. Millions of computer programmers are developing virus programs for your computer.
Start up with firewalls
Your computer comes with security system e.g. some operating systems provide security firewalls for the protection of system. When you start to use computer for the very first time, you have to register your software from its provider. You should make sure the proper functioning of your computer software. This will ensure the basic protection of your computer.
You can’t rely on a firewall
Your computer’s basic security can’t protect it from new emerging spam ware. Some software also provides virus protection tips to you for the additional computer protection. They stop the operations of harmful programs, but, they need regular updates. So, don’t be surprised to update on daily bases. Some are downloaded daily and some have to update at regular intervals.
Up-gradation of security system
Most of computer security software needs regular updates and reviews. Most of people use only basic security systems for their computers. Basic or free software need crucial updates. However, paid software for computer security offer more security options, new features and are very easy to use. Make sure that publisher is providing you proper services for the software. Well-known protection software provides full security reviews and virus protection tips at regular intervals.
Security risks
Mostly, users are not aware of risks related to spam ware and virus databases. Spy ware can steal your personal and important information, credit card numbers, and your shopping information. They further use illegal ways of sharing information. The bad spyware programs interfere with normal computer operations. Some virus programs redirect your internet browser to different web addresses and increase risks of infection.
Virus threats require your serious attention
A virus or spyware can replicate itself and stick to any document that you send to other computers. A virus can travel through internet via e-mail attachment, and can cause harm to millions of computers. When you are opening e-mails, it is necessary to scan before opening it. Most of people have no idea about how to deal with this type of situation. Some viruses and spyware are really hard to find out from your computer, because they are hidden in the document files. They change their names and act like your documents.
If you get an e-mail from unknown source or ask to download a file from internet that you are not familiar with, then avoid it and keep your security system updated. In addition, regularly update the database. Check it and save your computer from viruses and all spyware. The best way to protect your computer from viruses is to educate yourself about computer viruses and become familiar with software, which looks like malicious software.
Start up with firewalls
Your computer comes with security system e.g. some operating systems provide security firewalls for the protection of system. When you start to use computer for the very first time, you have to register your software from its provider. You should make sure the proper functioning of your computer software. This will ensure the basic protection of your computer.
You can’t rely on a firewall
Your computer’s basic security can’t protect it from new emerging spam ware. Some software also provides virus protection tips to you for the additional computer protection. They stop the operations of harmful programs, but, they need regular updates. So, don’t be surprised to update on daily bases. Some are downloaded daily and some have to update at regular intervals.
Up-gradation of security system
Most of computer security software needs regular updates and reviews. Most of people use only basic security systems for their computers. Basic or free software need crucial updates. However, paid software for computer security offer more security options, new features and are very easy to use. Make sure that publisher is providing you proper services for the software. Well-known protection software provides full security reviews and virus protection tips at regular intervals.
Security risks
Mostly, users are not aware of risks related to spam ware and virus databases. Spy ware can steal your personal and important information, credit card numbers, and your shopping information. They further use illegal ways of sharing information. The bad spyware programs interfere with normal computer operations. Some virus programs redirect your internet browser to different web addresses and increase risks of infection.
Virus threats require your serious attention
A virus or spyware can replicate itself and stick to any document that you send to other computers. A virus can travel through internet via e-mail attachment, and can cause harm to millions of computers. When you are opening e-mails, it is necessary to scan before opening it. Most of people have no idea about how to deal with this type of situation. Some viruses and spyware are really hard to find out from your computer, because they are hidden in the document files. They change their names and act like your documents.
If you get an e-mail from unknown source or ask to download a file from internet that you are not familiar with, then avoid it and keep your security system updated. In addition, regularly update the database. Check it and save your computer from viruses and all spyware. The best way to protect your computer from viruses is to educate yourself about computer viruses and become familiar with software, which looks like malicious software.
Labels:
Born To Hack,
hacks,
Master Of All Hacking Warez,
Mehta,
Shaify,
Shaify Borntohack,
Shaify master of all hacking warez,
Shaify Mehta,
shaify.com,
Virus,
Vista,
Windows 7
RSA's Art Coviello predicts 2012 to be the year of resiliency and adaptation

Credit: Wikipedia
RSA executive chairman Art Coviello said that if 2011 was the year of the attack, then 2012 will be the year of resiliency and adaptation within the industry.
In an open letter, Coviello said the company's experiences of this year "have indeed made us stronger and smarter".
“Our society has made unimaginable progress over the past 20 years through advances in information technology. It's our responsibility to sustain this advancement through a trusted digital world,” he said. He added that never in his career has he known CEOs and corporate boards to be as interested in security as they are now; and he cited one common theme: persistent, advanced and intelligent threats.
In an open letter, Coviello said the company's experiences of this year "have indeed made us stronger and smarter".
“Our society has made unimaginable progress over the past 20 years through advances in information technology. It's our responsibility to sustain this advancement through a trusted digital world,” he said. He added that never in his career has he known CEOs and corporate boards to be as interested in security as they are now; and he cited one common theme: persistent, advanced and intelligent threats.
Windows 8 picture security just a toy, claims RSA SecurID inventor

Credit: Victor Agreda Jr.
The Windows 8 feature that logs users in if they touch certain points in a photo in the right order might be fun, but it's not very good security, according to the inventor of RSA's SecurID token.
"I think it's cute," says Kenneth Weiss, who now runs a three-factor authentication business called Universal Secure Registry. "I don't think it's serious security."
The major downside of the picture password is that drawing a finger across a photo on a touch screen is easy to video record from a distance, making it relatively easy to compromise, he says. Designers of alphanumeric passwords recognise this danger, and have responded to it by having password characters appear as dots on the screen so the password can't be copied down.
"I think it's cute," says Kenneth Weiss, who now runs a three-factor authentication business called Universal Secure Registry. "I don't think it's serious security."
The major downside of the picture password is that drawing a finger across a photo on a touch screen is easy to video record from a distance, making it relatively easy to compromise, he says. Designers of alphanumeric passwords recognise this danger, and have responded to it by having password characters appear as dots on the screen so the password can't be copied down.
Source:
Friday, December 23, 2011
In Sweden, the Fiber optic up to 120 GBPS.....!!!!
In Sweden, a new record is being built around fiber optic ...
In Sweden, a scale experiment is taking place right now. Cisco and Telia (Swedish ISP) test a fiber network to go up to 120 Gbps! They even made an application for deposit in the Guinness Book to be recognized as the largest LAN parties in the world ...
To be eligible, it will exceed the 20,000 customers who are connected to the first phase and 750 000 for the second phase. This fiber will be drawn to a length of 300 km between Stockholm and Jönköping, thus taking all subscribers of this operator between the two cities. Telia is responsible for the fiber and equipment such as Cisco CRS-3, high-speed router that can handle up to 322 Tb / s.
Both partners explain that if the test is successful, it will be a new record for the networks and a new perspective for the use of new technologies. This will allow the 750,000 lucky to eg download a movie in high definition (legally, of course) in just 0.05 seconds! Subscribers' computers, however, should become limiting factors, the world upside down?!
And we, during that time, we dream of the widespread 100 Mbps FTTH throughout ...
And we, during that time, we dream of the widespread 100 Mbps FTTH throughout ...
Thursday, December 22, 2011
time for iOS 5.0.1
If you depend upon an unlock (you are not on the official carrier) and you own an iPhone 3GS or 4 then this is the time for you to have experience of iOS 5.0.1
The most awaited ultrasnow 1.2.5 (to unlock the iPhone 4 and 3GS on iOS 5.0.1) is out now. Just simply update to iOS 5.0.1 and go to cydia then install ultrasnow (make sure while installing ultrasnow your sim is out of the sim tray) reboot the phone and while rebooting put the sim back in and then wait it may take upto 3 minutes so be patient!!!!!
Supported Basebands
Note: the repository for ultrasnow is http://repo666.ultrasn0w.com (yes it is a zero in ultrasn0w)
add this repo on the iPhone (if you dont know please refer to some of the earlier posts).
So it is just a minor update for unlockable basebands to unlock the basebands that were unlockable earlier as well.
Enjoy the iOS experience.
Any comments or suggestions or any query please drop in at charanjit@borntohack.in.
The most awaited ultrasnow 1.2.5 (to unlock the iPhone 4 and 3GS on iOS 5.0.1) is out now. Just simply update to iOS 5.0.1 and go to cydia then install ultrasnow (make sure while installing ultrasnow your sim is out of the sim tray) reboot the phone and while rebooting put the sim back in and then wait it may take upto 3 minutes so be patient!!!!!
Supported Basebands
- 01.59.00
- 04.26.08
- 05.11.07
- 05.12.01
- 05.13.04
- 06.15.00
Note: the repository for ultrasnow is http://repo666.ultrasn0w.com (yes it is a zero in ultrasn0w)
add this repo on the iPhone (if you dont know please refer to some of the earlier posts).
So it is just a minor update for unlockable basebands to unlock the basebands that were unlockable earlier as well.
Enjoy the iOS experience.
Any comments or suggestions or any query please drop in at charanjit@borntohack.in.
Labels:
Born To Hack,
cydia,
Hack,
hacks,
iPhone,
Master Of All Hackig Warez,
Master Of All Hacking Warez .charanjit
Wednesday, December 21, 2011
Find Out the Time you have Worked on a Document or a Presentation

One of the things most writers want to know is how much time they’re spending on writing a piece of text. If you use Microsoft Word for all your writing needs, you’re in luck, because it is really easy to find out the time consumed on the editing of a Word document.
When you start working on a new Word document, a timer starts, and once you save the document, the time consumed thus far is saved as the ‘total editing time’. You continue to work on the document, and save it again, and the time elapsed since the last save is added to the total editing time. However, if you exit without saving the document, the time since the last save won’t be added to the total time. In our testing, this feature was found to be present in Office ’03, 07’, and ‘10.
So when you’re working on the document and want to check the total time consumed so far (since the beginning), click the Office logo, navigate to Prepare, and click Properties.

In the properties pane, click Document Properties>Advanced Properties.

In the properties window, click
Labels:
Aryan Gupta,
Aryan.Born To Hack,
Aryan.Master Of All Hackig Warez,
Born To Hack,
Doc,
Master Of All Hackig Warez,
Microsoft,
ppt,
Presentation,
Tricks And Tips,
Windows,
Word
How to implement Encryption/Decryption on Data ?
Data encryption is a method in which highly important and sensitive data is converted into unreadable form before its storage or transmission over the LAN/WAN. You can read encrypted data or decrypt it, if you have access to password or secret key.
Case Study: MCS folder have two files name mcs-morning and mcs-evening. User A wants to secure mcs-morning file from user B and all other users in the network. But user B also wants to secure mcs-evening file from user A and all other users in the network.
To implement this, first make a folder with name MCS folder and set NTFS permission as only administrator, user A, user B access MCS folder and administrator have full rights and user A and user B have modify permission on MCS folder. Now to secure files, login with user A and follow the given steps.
First open the MCS folder and right click on mcs-morning file then click on properties.

- Now click on advance button then check to encrypt content to secure data.
- Click Ok button then apply.

- Here system will ask you to secure the parent file and folder or only this file to secure data.
- Now click Ok button to finish the user A settings.
- Now to secure files, login with user B and follow the given steps.
- First open the MCS folder and right click on mcs-evening file then click on properties.
- Now click on advance button then check to encrypt content to secure data.
- Click Ok button then apply.
- Here system will ask you to secure the parent file and folder or only file to secure data.
- Now click Ok button to finish the user B settings.
- After implement encryption, user A can not read mcs-evening file and user B can not read the mcs-morning file.
Decryption of data
- First open the MCS folder and right click on mcs-morning file then click on properties.
- Now click on advance button then uncheck to encrypt content to secure data.
- Click Ok button then apply.
- Here your computer will ask you to decrypt the parent file and folder to insecure data then press Ok button to finish process.
Tuesday, December 20, 2011
How to Speed Up Windows Seven OS ?
With the release of Windows 7, Microsoft may just have introduced the fastest operating system in the world. For those speed junkies who are never satisfied, we have provided a few tips that will help you make your PC even faster.
Disable Automatic Disk Defragmentation
The Automatic Disk Defragmentation feature in Windows is designed to maintain the health of the operating system. However, it also makes Windows run a little slower. You can put an end to this by disabling the feature and manually running at your leisure. To do so, click “Start” and select “Computer.” Next, right click on your primary hard drive and select “Properties.” Lastly, select the “Tools” tab, click “Defragment Now” and uncheck the “Run on a schedule” option.
Utilize ReadyBoost
ReadyBoost is a built-in Windows 7 feature that allows you to use a USB flash drive to enhance system performance. How is this possible? The drive itself acts as additional computer memory!
In order to make use of this feature, you will need a USB drive with at least 2 GB of space. From there, you simply connect the drive to your computer, click “Start” and select “Computer.” Next, click on the USB drive and select “ReadyBoost.” Lastly, select “Use this device” and choose as much capacity as possible below on the “Space to reserve for system speed” slide.
Disable Windows Transparency
The transparency of windows is a great perk from a presentation aspect, but this may not be the case for those with older hardware as it can drastically impact performance. The good thing is that transparency can be disabled with ease. Simply right-click on your desktop, select “Personalize,” choose the active theme and then navigate to “Windows Color.” Finally, uncheck the “Enable Transparency” option.
Disable Unwanted Features
There may be numerous Windows 7 features that you really don’t need. These same features could also slow down your computer. To disable them, click on “Start,” choose “Control Panel” and then select “Programs and features.” Next, select the “Turn Windows features on or off” option, navigate through the list and uncheck all the features you want to disable. Once you are done, simply click “OK” to remove those features.
Disable Startup Services
Startup services are notorious for slowing down performance in XP and Vista. The same holds true for Windows 7. You can disable unwanted services by hitting “Start,” typing “msconfig” in the search bar and clicking “Enter.” Click the “Services Tab” on the next window and deselect the services you do not want to automatically run at startup. While this all depends on preference, services that impact performance the most include “Offline Files,” “Tablet PC Input Services,” Terminal Services,” “Fax” and “Windows Search.”
Disable Minimizing/Maximizing Animations
Many users have already fallen in love with the minimizing and maximizing animation effects of windows. However, some may find it irritating after a while as it can eventually lead to slowdowns. If you want to disable this function, hit “Start,” enter “System Properties Performance” in the search bar and click “OK.” On the next screen, deselect the “Animate window when minimizing and maximizing” option and click “OK.”
Update Your Windows 7 Drivers
Lastly, ensure that you have the latest device drivers made specifically for Windows 7. Since your PC can have hundreds of drivers installed in it at any given time, this task can be tedious. Luckily there are 3rd party utilities out thee such as DriverFinder™, which can greatly speed up this process.
Labels:
Security,
Tricks And Tips,
Windows 7
Monday, December 19, 2011
How To Store More Files On Dropbox Than Your Permitted Sapce
I have been using the cloud storage and file synchronization service Dropbox more frequently lately, and its is pretty awesome.
You probably know that Dropbox keeps track of all file changes automatically, with options to restore a previous version of the file. While looking at that I noticed that it is possible to restore deleted files as well. I first thought about writing an article about that as it is a pretty interesting feature. Especially so for users who have accidentally deleted files, and users who want to make sure that deleted files cannot be recovered. A recoverable copy on the Dropbox server is the last thing those users would want.
While I was investigating the issue I noticed that Dropbox subtracts the file size of deleted files from the available ratio. This basically means that you get additional upload space even though the files are still stored on Dropbox. Remember, deleted files do not get deleted right away.
The Dropbox FAQ states that deleted files and old file versions get saved for 30 days by the service before they are removed.
I also tested if it is possible to restore deleted files to get beyond the allowed quota of an account. Turned out that this is actually possible as well. Here is how it is done in detail.
Go to the Dropbox website and log into your account there. Switch over to Files to see all your files currently stored on Dropbox. Activate the show deleted files button to display deleted files and folders in the file listing. These are highlighted in grey, and the size says deleted instead of the real file size.
The idea is this. You upload files as usually to Dropbox. Once you come near the quote you start deleting files. Don’t worry, the files are still there. Your quote drops again and you can upload more files to Dropbox. I’m not sure if there is a limit or if you could theoretically go on forever. You can later on restore deleted files which can move you over your Dropbox quote.
You basically have two options to go upload more files to Dropbox than your quote allows.
Delete files temporarily to reduce the storage quota
Recover the files again at a later time to store files over the quota
Please note that deleted files won’t be synchronized, and that no new file versions will be saved by Dropbox. Have other Dropbox tips to share? Let me know in the comments.
Labels:
Aryan Gupta,
Aryan.Born To Hack,
Aryan.Master Of All Hackig Warez,
Born To Hack,
Dropbox,
Ethical Hacking,
Hacking,
hacks,
Master Of All Hackig Warez,
Security,
Tricks And Tips
Hide All Google Chrome Tabs With A Single Click
If you are working in a multi-user office or in a room that people may enter unannounced, you’d probably like an option to hide what’s shown on the screen when that happens. Maybe you like buying gifts for someone online, like to surf on a site that you are not allowed to access, or do not want your office colleagues to find out that you are into Britney Spears. Whatever it is, a Panic Button application can be the solution.
 A panic button or boss key application performs one or multiple actions when the button is activated. This usually includes hiding a window, but sometimes other things such as muting the volume.
A panic button or boss key application performs one or multiple actions when the button is activated. This usually includes hiding a window, but sometimes other things such as muting the volume.The Google Chrome Extension PanicButton adds the functionality to the Chrome browser. It basically allows you to hide all open Chrome tabs with a single click.
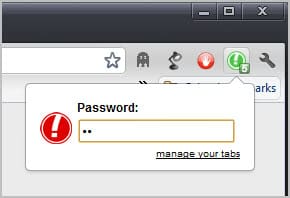
Here is how it works in detail. The extension adds a single button to the Chrome address bar upon installation. A left-click on the button hides all open tabs and displays a single blank tab instead in the browser interface. A second left-click loads the websites again so that you can continue using them. The extension saves the open tabs to bookmarks. This means that you may lose whatever you have been working on before you have clicked on the button.
A green icon with the number of saved tabs attached to it is displayed when the panic button has been activated.
New users should take a look at the options of the extension by right-clicking on the icon and selecting options from the context menu.
Here it is possible to set a password to protect tabs from being restored. Anyone could theoretically click on the button to recover tabs otherwise.
You can furthermore change the default keyboard shortcut from F4 to another combination. Please note that you can only use the shortcut on http or https pages. It wont work on blank or internal pages.
Safe pages, that is pages that are displayed when the panic button is activated, can be configured in the options as well. You can select to display new tab, empty or custom pages. Custom pages are websites that you need to enter. These are then loaded whenever the panic button is activated in the browser.
The hide panic button option finally hides the button once it has been activated. This removes the indication from Chrome’s toolbar.
Chrome users can download the PanicButton extension from the Google Chrome Extension repository.
Tuesday, December 13, 2011
How to make faster windows XP shutdown process?
Using this tip, you can make the windows XP shutdown process bit faster up to 50 percent than normal time. Normally windows XP takes time to close all running services and applications to complete the shutdown process, but if you have little experience to edit windows registry keys then you can easily manage the windows shutdown process.
Perform the following steps to manage the windows shutdown process:
- To edit this feature, you will need to be logged into your computer with administrative rights.
- First click on Start button to open "Run" and type "notepad" then press Ok button to open the Notepad Editor.
Now type the following code in Notepad.
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\ControlPanel\Desktop
"AutoEndTasks"="1"
"HungAppTimeout"="1000"
"WaitToKillAppTimeout"="2000"
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control
"WaitToKillServiceTimeout"="2000"
"AutoEndTasks"="1"
"HungAppTimeout"="1000"
"WaitToKillAppTimeout"="2000"
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control
"WaitToKillServiceTimeout"="2000"
Save this file with .exe extension (as registry file, for example shutdown.exe).
Now double click on shutdown.exe file (in this case), and click Yes and again Ok button to update computer registry.
Thursday, December 8, 2011
Springtomize 2 for iOS 5
Springtomize 2 customized for the iOS 5 is now out. It is better than the previous release.
Features it provide:-
For Now its a paid application in cydia but if you want it for free here's how
Features it provide:-
- Changing the Animations
- Change Dock Settings
- Lock Screen customization
- Icons customization
- Folder Customisation
- Multiple pages customization
For Now its a paid application in cydia but if you want it for free here's how
- Go to Cydia.
- Open the Manage Tab (On the Bottom of the Screen 4th option).
- After that open Sources.
- In the sources tap on Edit (Top Right Corner of the screen).
- The Tap Add (Visible on top Left of the screen when you tap Edit).
- Now Enter the url http://www.sinfuliphonerepo.com.
- After getting the repository added now go to the repository.
- Search for Springtomize 2 cracked and there it is all free for u.
- So Enjoy Customizing your iDevice.
Tuesday, December 6, 2011
update iDevice to iOS 5.0 with iPad Baseband
The new and revolutionary iOS 5.0 is here and here is how to update and jailbreak and unlock the device running on iOS 5.0

The hardware / software you would require:-
1) iDevice
2) iOS 5.0 firmware(link).
3) redsnow (link here to download for mac and download for windows)
instructions for Windows Users:-
instructions for Mac Users:-
If you are on iPad or iPod then you can skip off the last step of installing ultrasnow as this will not be required..........

The hardware / software you would require:-
1) iDevice
2) iOS 5.0 firmware(link).
3) redsnow (link here to download for mac and download for windows)
instructions for Windows Users:-
- Open Rednsow and then press extras (turn off your device before that) and go in Pwned DFU mode by following the instructions on the screen.
- Once in Pwned DFU mode, Open iTunes and press shift+restore and select the iOS 5.0 firmware that you just downloaded.
- Restore the iPhone. (if there is any error mail me the error code, i will mail you the procedure to remove it.) email-id- charanjit@borntohack.in
- Once restored the firmware then you would want to skip setup because it asks for the Sim (if you are not on the official supported carriers) open redsnow once again.
- in Redsnow go to Extras->Select ipsw-> back-> jailbreak-> check install cydia->(turn off the device)next-> follow the steps on the screen and then the device will reboot.
- Now go ahead and setup the device it will not ask for the Sim and Cydia would be installed.
- Now in Cydia install ultrasnow 1.2.4 and unlock the iDevice and enjoy any Sim.
instructions for Mac Users:-
- Open Rednsow and then press extras (turn off your device before that) and go in Pwned DFU mode by following the instructions on the screen.
- Once in Pwned DFU mode, Open iTunes and press alt+restore and select the iOS 5.0 firmware that you just downloaded.
- Restore the iPhone. (if there is any error mail me the error code, i will mail you the procedure to remove it.) email-id- charanjit@borntohack.in
- Once restored the firmware then you would want to skip setup because it asks for the Sim (if you are not on the official supported carriers) open redsnow once again.
- in Redsnow go to Extras->Select ipsw-> back-> jailbreak-> check install cydia->(turn off the device)next-> follow the steps on the screen and then the device will reboot.
- Now go ahead and setup the device it will not ask for the Sim and Cydia would be installed.
- Now in Cydia install ultrasnow 1.2.4 and unlock the iDevice and enjoy any Sim.
If you are on iPad or iPod then you can skip off the last step of installing ultrasnow as this will not be required..........
Labels:
apple,
Baseband,
Born To Hack,
Borntohack News,
charanjit,
Charanjit Singh Bhalla,
iOS5,
iPad,
iPhone,
IPod Stuff,
Mac OS,
Master Of All Hackig Warez,
Master Of All Hacking Warez .charanjit
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)

Stuffs
- Android (12)
- Antivirus (3)
- Backtrack (13)
- Borntohack News (5)
- Cracking (6)
- cydia (2)
- Ethical Hacking (17)
- Facebook (47)
- Filesonic Premium Accounts (3)
- Firefox (34)
- Google (66)
- Google+ (8)
- Hacking (220)
- hacking tools (4)
- Hotfile Premium Accounts (1)
- iOS4 (11)
- iOS5 (6)
- iPad (25)
- iPhone (55)
- IPod Stuff (38)
- javascript (23)
- Linux (7)
- Metasploit (2)
- Mobile Stuff (48)
- Registry Hacks (43)
- Security (106)
- Tech News (182)
- Tricks And Tips (512)
- Trojan (5)
- Unlocking (2)
- Windows (68)
- Yahoo (5)
Facebook :
Translate Website
Follow On Buzz
Hacking Purity Test Solutions
Subscribe Email :
Blog Archive
-
▼
2011
(768)
-
▼
December
(19)
- Borntohack Members Wishes You , Happy New Year ...!!!
- iMessages going to stolen iPhones? There may be a ...
- Occupy Geeks Are Building a Facebook for the 99%
- 2011 is the Year of the Hacktivist, Verizon Report...
- Use your picture to log in into Windows8
- How to tag a friend or a page on Facebook on mobil...
- Virus protection tips: from basic to advanced level
- RSA's Art Coviello predicts 2012 to be the year of...
- Windows 8 picture security just a toy, claims RSA ...
- In Sweden, the Fiber optic up to 120 GBPS.....!!!!
- time for iOS 5.0.1
- Find Out the Time you have Worked on a Document or...
- How to implement Encryption/Decryption on Data ?
- How to Speed Up Windows Seven OS ?
- How To Store More Files On Dropbox Than Your Permi...
- Hide All Google Chrome Tabs With A Single Click
- How to make faster windows XP shutdown process?
- Springtomize 2 for iOS 5
- update iDevice to iOS 5.0 with iPad Baseband
-
▼
December
(19)
Discussion Here ..!!!
SMS Subscribe
Security Alerts
Pages
Total Pageviews
Network Blogs
Get Domain Here :-
All Rights Reserved. http://borntohack.in Designed By Shaify Mehta